Collection of Coins of the Qarakhanid
| The
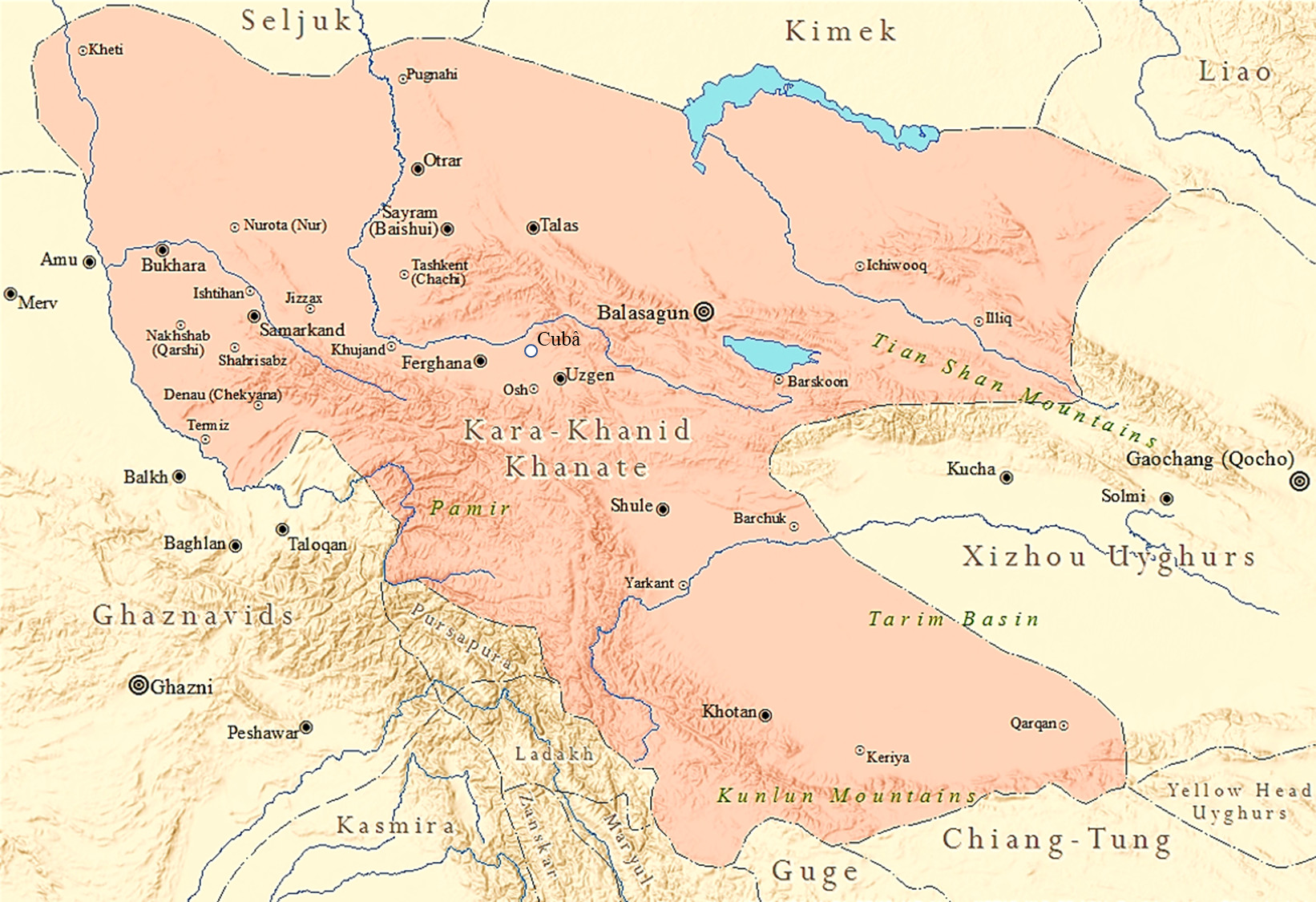
Kara-Khanid Khanate (Persian: قراخانیان, romanized: Qarākhāniyān),
also known as the Karakhanids Qarakhanids, Ilek Khanids or the
Afrasiabids (Persian: آل افراسیاب, romanized: Āl-i Afrāsiyāb, lit.
'House of Afrasiab'), was a Turkic khanate that ruled Central Asia in
the 9th through the early 13th century. The dynastic names of
Karakhanids and Ilek Khanids refer to royal titles with Kara Kağan
being the most important Turkic title up till the end of the dynasty. The Khanate conquered Transoxania in Central Asia and ruled it between 999–1211. Their arrival in Transoxania signaled a definitive shift from Iranian to Turkic predominance in Central Asia, yet the Kara-khanids gradually assimilated the Perso-Arab Muslim culture, while retaining some of their native Turkic culture. The capitals of the Kara-Khanid Khanate included Kashgar, Balasagun, Uzgen and Samarkand. In the 1040s, the Khanate split into the Eastern and Western Khanates. In the late 11th century, they came under the suzerainty of the Seljuks, followed by the Kara-Khitans in the mid-12th century. The Eastern Khanate was ended by the Kara-Khitans in 1211. The Western Khanate was extinguished by the Khwarazmian dynasty in 1213. Wikipedia |

